A phone charger is often referred to as a “power adapter” or “charging brick”, and its main function is to provide the necessary power to recharge a phone's battery at any time. Charging efficiency and safety are the key factors that differentiate phone chargers. To better understand them, diving into basic knowledge is an important step.
How to read the specifications of a phone charger

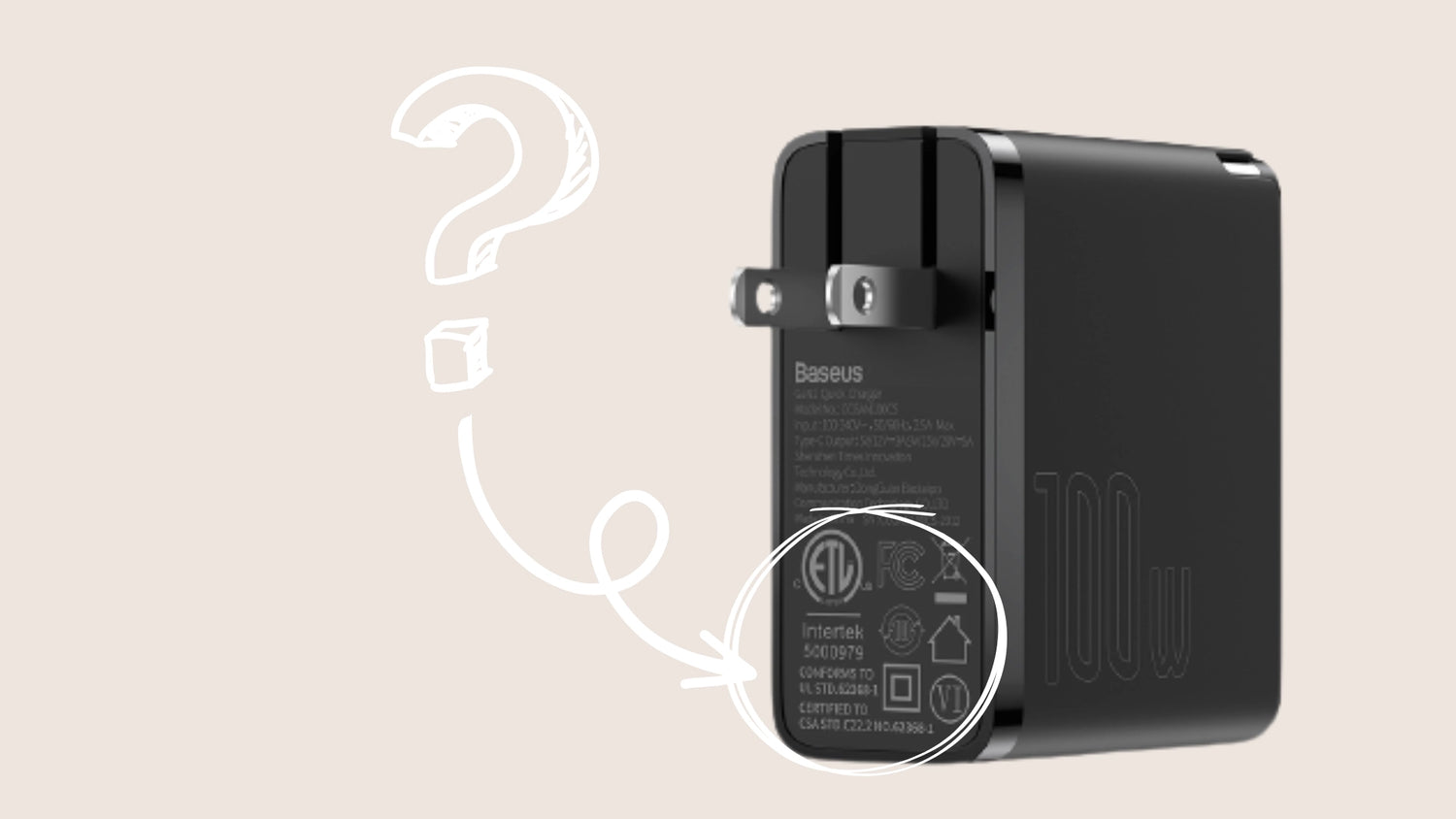
Icons Explanation
1) Look for these symbols or icons
FCC, ETL, ⧈, No trash, House, 10-Year Circled, VI
Double Insulation

The sign “square in a square” refers to “Double Insulated”.
- Double insulation refers to the use of both working insulation (basic insulation) and protective insulation (backup insulation). Working insulation is designed to allow the device to work properly and protect it against electric shock, while protective insulation serves as a backup to prevent electric shock in case the working insulation fails.
- Electric appliances with double insulation are Class II equipment. Insulation should be reinforced on the power cord of Class II equipment. The symbol ⧈ should be printed on a conspicuous place. Insulation resistance of working insulation of Class II equipment shall not be less than 2MΩ, insulation resistance of protective insulation shall not be less than 5MΩ, and insulation resistance of strengthened insulation shall not be less than 7 MΩ.
DO NOT Dispose (Crossed Trash Can)

The WEEE symbol is a reminder that this item should not be disposed of with regular household waste. It is required to be properly categorized and recycled to prevent pollution and to conserve resources.
Indoor Use Only

The side where prongs fold in is where specifications and the little house icon are printed. The “Indoor Use Only” means that the use of the equipment outside could result in dangerous outcomes.
As a charger dissipates heat, it requires appropriate ventilation and should be kept away from flammable and explosive substances. Indoor use only can be interpreted as if a charger gets in contact with rain, it will damage the charger as well as the battery of devices being charged, and may result in potential fire hazard. In summary, keep the charger away from liquid or exposed to direct sunlight for an extended time.
10-Year Reassurance Period

Electronic products contain toxic and harmful substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium. The icon with 10 wrapped in circular arrows indicates that this charger is 10-year guaranteed safe from leak or mutation of those toxic and harmful chemical substances. The 10-year icon refers to its “reassurance period” rather than the product quality guarantee period. Once 10 years have passed, these substances may leak or mutate, causing pollution to the environment, or serious harm to human health and property. Reassurance period means that all electronic products are safe to use within this period, and manufacturers will no longer be responsible for product quality issues that occur after the 10 year period.
FCC Mark

FCC is short for Federal Communications Commission of the United States, the institution that regulates the import and use of radio frequency devices, including computers, fax machines, electronic devices, radio receiving and transmitting equipment, and other products that may harm personal safety. The above-mentioned products exported to the United States must be tested and approved by a government-authorized party in accordance with FCC technical standards.
VI Energy Efficiency

The icon with the roman numerals V or VI inside a circle is a symbol for energy efficiency certification. "V" represents a five-level energy efficiency rating, while "VI" represents a six-level energy efficiency rating, the most efficient. This symbol is used to indicate the energy efficiency level and performance indicators of energy-using products, providing necessary information for users and consumers to make purchasing decisions and guiding them to choose energy-efficient products.
ETL Certification

The ETL mark on electrical, mechanical, or electromechanical products signifies that the product meets the minimum requirements of recognized product safety standards in the United States and Canada, and has been tested accordingly. Additionally, ETL requires that the production environment is inspected, and the manufacturer agrees to conduct regular follow-up inspections of its factory to ensure ongoing compliance with these requirements.
2) Other type of certification
CE Certification

CE is a mandatory certification mark for products exported to territories member of the European Union. It is a passport for manufacturers to enter the European market. Only products with the "CE" mark can be sold in europe. It is a safety pass mark, not a quality pass mark.
RoHS Certification

RoHS is a mandatory standard established by EU legislation, which stands for "Restriction of Hazardous Substances." The purpose of this directive is to limit the use of hazardous substances, including lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls, and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in electrical and electronic equipment. Portable power banks that fail to comply with this standard are not permitted to enter the EU market.
UL Certification

UL certification is a globally recognized mark of safety and quality. UL stands for Underwriters Laboratories, a leading organization that provides independent testing and certification services for a wide range of products. UL is one of the largest private institutions of its kind in the world, and products exported from the United States or products entering the US market must have this mark.
3) Fundamental knowledge on input and output
Input specifications
I believe we are all familiar with those texts mushed together printed on electronics including model, input output voltage, current, certification icon, 100-240V, and all that technical information.
What do they mean?

Input specs for chargers are in the format "AC 100V-240V 50/60Hz xA". This means the charger can be used with an AC power outlet in the range of 100V-240V and a frequency of either 50Hz or 60Hz. The maximum current the charger can handle is xA, and the input current varies from 0.5A to 1.5A depending on the model. A charger acts as a "power control station," converting the high-voltage current to a level adequate for a mobile phone before it reaches its destination.
Input voltage refers to the working voltage of the charger when it is plugged into a socket to supply power. All civilian electricity in the world uses AC current, within a voltage range of 100V-380V, while residential single-phase electricity generally ranges from 100V to 240V. Chargers are compatible with both 50Hz and 60Hz frequencies.
In human language, it’s designed to be used in every corner of the world.
Another factor is that plug specifications vary in different countries and regions according to the electrical power system. If the plug is not compatible, it cannot be plugged in even if the voltage is suitable. 
All our current chargers support 100V-240V working voltage, fulfilling the demand of wide voltage, and are compatible with the two major voltage systems of 220V and 110V. Some design margins can even support 90V-264V working range. This kind of charger that supports 100V-240V working voltage can be well adapted to the local electricity whether it is used at home, packed in for a short trip or even for international travels.
Recap on input specification
- Chargers operate on different working voltages including 100V-240V, 100-120V, 200-240V, and etc.
- 100V-120V and 200-240V are designed to only work in a single electrical power grid. They are generally used to improve products with higher power density. Users do not need to worry as long as they only use them at home.
- 100V-240V wide range voltage covering 110V and 220V the two mainstream electrical power grid systems, can also be used for cross-region travel, and meanwhile is the working voltage used by top ranking chargers in the market. Another point to pay attention as well is what standard does the local plug adopt. Packing with a plug adapter is always the right way to travel.
Output specification
Charger’s power output is the main to zoom in. It involves output voltage and output current, thus the maximum output power a charger could provide requires multiplying both. The equation goes: Power output (W) = current (A) X voltage (V);
- Charger will first convert the 220V electricity from a socket to 5V or other voltage output for smartphones;
- Circuit in mobile phones restrains power to ±4.3V before it reaches the battery.
- That is 2 steps of voltage weakening.
Fast Charging Conditions:
Phone + Charger + Charging Cable all support the same fast charging protocol
4) Process of charger replenishing a smartphone
Explanation
- 100-240V high voltage is converted to low voltage of 5V, 9V, 12V, 20V, and more
- Charger supplies power to phone through different voltage and current level
(5V-1A, 5V-2A, 9V-2A, 12V-1.5A);
- Power management chip in smartphone controls charging process through 3 stages
a: Constant current stage
b: Constant pressure stage
c: Trickle stage
- Chargers are designed to mandatory run protocol detection, temperature detection, remaining power detection, cable resistance detection and more routines before starting to charge device (s) constantly.
Bear in mind that fast charging is about boosting the speed from 0% to 80% battery, especially from 0%-50% which is drastically faster than using a standard charger. It is indeed NOT fast charging all the way to 100%.
NOTE: A constant feed of high current easily accumulates dendritic crystals over time, growing into lithium dendrites near the negative electrode of a lithium-ion battery. When the dendrites grow, they will eventually pierce the diaphragm between the positive and negative electrodes, causing a short circuit. It’s a protection for the battery to restrain the speed after fast charging for a while.

Why it’s not fast charging

- Battery percentage: fast charging is for battery <50%, the higher it is the slower it gets.
- Phone temperature: heat control chip limits speed to protect battery even if criteria 1 is met.
- Cable: it has to support fast charging protocol and the current load.
- No protocol match: replug if phone, cable, charger, battery level, and temperature meet conditions.
- Output only peaks for charging from 0%-50%, then gradually decreases.
In conclusion, understanding the specifications of a phone charger is important to ensure that it's safe and efficient to use. Look for certification symbols, make sure the input and output specifications match the device being charged, and follow the manufacturer's instructions for safe use. By doing so, you can extend the life of your devices and avoid potential safety hazards. Shop Baseus' certified chargers to ensure your safety!
 United States/English
United States/English










2 comments
Denner Freire
Good reading!
Helpful for anyone that wants to get some knowledge of how charger works and even keep this information in consideration for charger purchases.
Good reading!
Helpful for anyone that wants to get some knowledge of how charger works and even keep this information in consideration for charger purchases.
Joyce
Good Essay!
Good Essay!